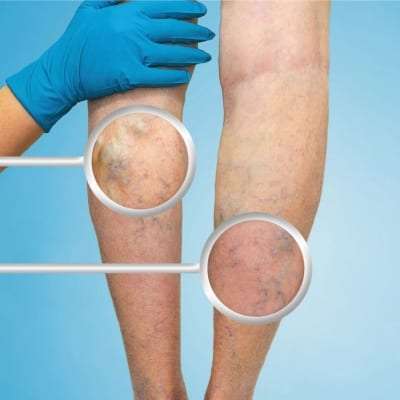
 Chronic Venous Disease (CVD) refers to conditions related to, or caused by, veins that become diseased or abnormal. Restless leg syndrome, varicose veins and spider veins are what most people think of when they hear the term Chronic Venous Disease. However, many vein conditions can cause pain or a feeling of ‘heaviness’ in the legs. Additionally, CVD can cause swelling and produce symptoms like numbness, weakness, or tingling in the affected area.
Chronic Venous Disease (CVD) refers to conditions related to, or caused by, veins that become diseased or abnormal. Restless leg syndrome, varicose veins and spider veins are what most people think of when they hear the term Chronic Venous Disease. However, many vein conditions can cause pain or a feeling of ‘heaviness’ in the legs. Additionally, CVD can cause swelling and produce symptoms like numbness, weakness, or tingling in the affected area.
Novus Spine & Pain Center vein clinic in Lakeland offers pain management treatments to help improve vein health and circulation. The treatments include minimally invasive procedures such as thermal ablation, RF ClosureFAST, and VenaSeal.
Chronic Venous Diseases
There are many vascular diseases that can cause pain. The signs and symptoms vary depending on the underlying cause. Generally, the symptoms include pain, swelling, and tenderness. Some of the diseases include:
- Buerger’s Disease is a rare condition that most often affects the small and medium-sized arteries and veins in the arms and legs. The veins swell and may develop clots, cutting off blood supply to the feet, toes, hands, or fingers. These body parts will hurt, even when resting. With severe blockages, the tissue may die (gangrene) and require amputation. Superficial vein inflammation and symptoms of Raynaud’s occur commonly in patients with Buerger’s Disease.
- Chronic Venous Insufficiency (CVI) is a condition that occurs when the venous wall and valves in the leg veins are not working efficiently, making it difficult for blood to return to the heart from the legs.
- Deep-Vein Thrombophlebitis is a serious condition that may first have less-pronounced symptoms (half of all cases have no symptoms). However, it carries the risks of a pulmonary embolism (when a clot detaches from the vein and travels to the lung) and chronic venous insufficiency (impaired outflow of blood through the veins). The condition results in dermatitis, increased skin pigmentation, and swelling. A large embolism can be fatal. Post-thrombotic syndrome can occur after a deep-vein thrombosis. The affected leg or arm can become chronically swollen and painful with skin color changes and ulcer formation around the foot and ankle.
- Edema (swelling in the legs) is an abnormal accumulation of fluid in the tissues of the body causing aching or a sensation of heaviness in the legs. The skin above the affected veins may itch, and there may be skin discoloration and ulcers on the inner aspect of the ankles (in advanced cases).
- Erythromelalgia is a rare peripheral vascular disease. Symptoms include burning pain, increased temperature, erythema (superficial reddening of the skin), and swelling. The condition affects the feet more often than the hands.
- May-Thurner Syndrome (MTS) is a condition that occurs when the left iliac vein is compressed by the right iliac artery, which increases the risk of deep-vein thrombosis (DVT) in the left extremity. Together, these left and right iliac veins drain blood from the pelvis and lower limbs. MTS is most common in women ages 20-40, especially after pregnancy.
- Nighttime Leg Cramps are a sudden tightening of calf muscles, especially during a run or when in bed.
- Pelvic Congestion is a condition similar to varicose veins that affects the veins in the pelvis. The vast majority of cases occur in women between the ages of 20 and 45 who’ve had multiple pregnancies.
- Peripheral Venous Disease occurs when valves inside the veins become damaged and do not close completely; therefore, blood does not flow back to the heart properly. This can cause pooling of blood or swelling in the veins. The veins bulge and appear as ropes under the skin. As blood moves more slowly through the veins, it may stick to the sides of the vessel walls and allow blood clots to form.
- Raynaud’s Phenomenon (Raynaud’s Disease or Raynaud’s Syndrome) is a condition that causes the small arteries of the fingers and sometimes the toes to twitch or cramp when the patient becomes cold or excited. It can temporarily shut down blood supply to the area, making the skin look white or bluish, and feel cold or numb. The symptoms include intermittent pain in the legs and feet or arms and hands, inflammation along a vein just below the skin’s surface due to a blood clot, and painful and open sores on toes and fingers.
- Restless Leg Syndrome (RLS) is a neurological condition associated with abnormal sensations in the legs and an urge to move the legs.
- Spider Veins are a chronic dilatation of the capillaries and other small blood vessels. Spider veins are smaller than varicose veins, but visible through the skin.
- Stasis Dermatitis (Discoloration) is a common inflammatory skin disease of the lower extremities in people with reduced blood flow.
- Superficial Thrombophlebitis is the inflammation of a vein near the surface of the skin in an extremity (especially the legs) that occurs in response to a blood clot in the vessel. A relatively minor disorder that causes red and tender veins.
- Varicose Veins are enlarged, swollen, and twisted veins that bulge from pools of blood that collect in the vein. They are visible through the skin, and usually blue or dark purple in color.
- Venous Ulcers are open skin sores, most often on the legs, but can appear on any part of the body. The sores are slow to heal because of poor blood circulation.
Diagnosing Chronic Venous Disease
Pain management doctors use duplex ultrasound to diagnose chronic venous disease. Duplex ultrasound shows how blood moves through the blood vessels. The term “duplex” refers to the fact that a duplex ultrasound uses both Doppler and conventional ultrasound imaging. The imaging helps in diagnosing arteriosclerosis (thickening or hardening) of the arteries, blood clots, deep vein thrombosis, (DVT), and venous insufficiency.
Treating Chronic Venous Disease
Treatment of chronic venous disease is based on the age of the patient as well as the symptoms. The primary goal is to stop swelling and prevent leg ulcers which can develop because of weak blood circulation. A compression bandage or stocking is the most common treatment should a leg ulcer develop. If an ulcer becomes infected by bacteria, antibiotics may be prescribed to kill the infection. A moist dressing over the ulcer may help it heal more quickly.
Medications
Your doctor may prescribe an antibiotic to treat infections or leg ulcers. Sometimes, your physician may also prescribe medication to help prevent blood clots. Blood thinners (anticoagulants) are the most common treatment to keep a clot from growing or breaking off, while also preventing new clots from forming. Despite the name, they don’t thin blood or dissolve existing clots. However, they do make it hard to stop bleeding from a minor injury.
Lifestyle Changes
Doctors will encourage patients to be physically active to help improve blood flow in the leg veins. Some of the advice includes:
- Movement. Try to avoid sitting or standing for an extended time. If you must sit for a while, stretch or wiggle your legs, feet, and ankles often to help the blood flow. If you stand a lot, take breaks to sit and put your feet up. This helps lower pressure in your leg veins.
- Exercise. Working out helps pump the blood. Walking is a good exercise, and is a simple way to make your legs stronger and help boost blood flow.
- Compression stockings. Elastic stockings place pressure on your legs to help blood flow. They come in varying degrees of tightness, lengths, and styles. Your doctor can suggest which might work best for you.
Minimally Invasive Medical Procedures
Minimally invasive medical treatments include:
- Endovenous ablation (endovenous thermal ablation) is an image-guided minimally invasive procedure to treat varicose veins. Endovenous ablation uses laser energy, radiofrequency, or steam to cauterize (burn) and close varicose veins. The procedure damages the vein, causing it to collapse, shrink, and eventually dissolve and disappear. Blood then flows through other nearby veins.
- Phlebectomy is a minimally invasive procedure that uses a small scalpel or needle to remove varicose veins just beneath the surface of the skin. The procedure is more effective than vein ligation and vein stripping. There is minimal discomfort and downtime. The patient can walk and resume a normal routine the day following the procedure.
- RF ClosureFAST. The ClosureFast Endovenous Radiofrequency Ablation procedure is a minimally invasive pain management treatment for venous reflux disease. The procedure uses radiofrequency energy to precisely and effectively treat patients suffering from varicose veins and other chronic venous insufficiencies. The physician inserts a special sheath into the varicose vein and uses intense heat to destroy it. The heat shrinks, collapses, and closes the vein.
- Sclerotherapy is a popular minimally invasive procedure dating back to the 1930s to make small varicose veins fade away. Sclerotherapy works by injecting a solution into a problem vein causing the vein to scar and fade away. This forces blood to flow through healthier veins. Over time, your body absorbs the scarred vein.
- VenaSeal is the only non-thermal, non-sclerosant (injected irritant) procedure approved by the FDA for use in the U.S. for closing diseased veins. It does not require heat to close a vein and therefore does not present the risk of burns and nerve damage. The system injects a special medical-grade adhesive into a diseased vein to seal it and prevent blood from flowing through it in the future.
Surgery
Fortunately, fewer than 10% of patients require surgery for CVD. When surgery is necessary, some of the options include:
- Ligation is a procedure whereby a damaged vein is cut and tied off so blood can’t flow through it. Depending on the condition, the doctor may remove a vein that is very damaged.
- Vein transplant is a procedure to replace a problem vein with a healthy vein taken from a different part of the patient’s body.
- Vein bypass is performed on veins in the upper thigh and only in the most severe cases. The doctor takes part of a healthy vein from another part of the body that is used to reroute blood around the affected vein. A hospital stay of 2-5 days is usually required for this type of procedure.
Prevention of Chronic Venous Disease
There are a variety of ways to help prevent chronic venous disease through lifestyle changes. Some of the suggestions are to:
- Quit smoking.
- Lose weight.
- Control chronic conditions such as high blood pressure and diabetes.
- Take aspirin to prevent blood clots.
- Reduce the amount of salt in your diet.
- Exercise regularly.
- Keep your legs elevated when possible.
Novus Spine & Pain Center
The Novus Spine & Pain Center vein clinic is in Lakeland, Florida, and specializes in treating chronic venous disease. By using a comprehensive approach and cutting-edge therapies, we work together with patients to restore function and regain an active lifestyle, while minimizing the need for opiates.
Our Mission Statement: To provide the best quality of life to people suffering from pain, by providing state of the art treatments, knowledge and skill, compassion, and respect for all.
For your convenience, you may schedule an appointment online, request a call back, or call our office at 863-583-4445.
Lakeland Vein Clinic Resources
Vein Conditions Producing Orthopedic Leg Pain (Novus Spine & Pain Center)
What is Chronic Venous Disease? (American Venous Forum)
What Is Chronic Venous Insufficiency? (WebMD)
Vascular Diseases and Pain (WebMD)
What Is a Venous Skin Ulcer? (WebMD)
Updated: October 7, 2021

